Optical Bandpass Filters are used to selectively transmit a portion of the spectrum while rejecting all other wavelengths. Optical Bandpass Filters are ideal for a variety of applications, such as fluorescence microscopy, spectroscopy, clinical chemistry, or imaging.
An optical bandpass filter has a transmission band surrounded by two blocking bands that allow only a portion of the spectrum to pass. These optical bandpass filters have broad spectral bandwidths in either the ultraviolet, visible, or infrared spectrums. The nearly black filters absorb visible radiation. They are perfect for ultraviolet or infrared detection applications. UV filters are often used to selectively transmit the 254nm and 365nm mercury lines. IR filters are often used in nightvision and IR sensing systems.
Color Separation Filter,Neutral Density Filter,Filter,Short/Long Wave Pass Filter,Bandpass Filter and Interference Filter available upon request.
Specification of our color filter as follow:
Optical Bandpass Filter,Optical Glass Bandpass Filter,Bandpass Filter Kits,Uv Bandpass Filter China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.opticsrealpoo.com
Keywords: acid etching; alkali etching; aluminum dissolution; extrusion marks; coarse grain; weld line.
1, process introduction
In recent years, the production and sales volume of aluminum alloy matt profiles has been increasing, with a market share of over 80%. At present, the production of matt profiles generally uses alkaline etching methods, and the aluminum dissolved losses range from 3% to 5%, which results in huge waste of resources, greatly increases the difficulty of environmental protection management, and aggravates the “three wastes†processing burden of the company. Acid etching technology is developed for the lack of alkali etching method, in principle, completely different from the alkaline pitting matt surface treatment. The process mainly adopts a unique method to generate a highly uniform and high-density molecular point corrosion on the surface of the aluminum profile, and by improving the material structure of the uneven surface of the profile, thereby achieving the effect of smoothing the surface and eliminating the surface defects caused by the metallurgical process (for example, eliminating the extrusion Indentation, masking of the weld line, and mitigation of defects such as coarse grains, make the aluminum surface smooth and delicate, soft metallic luster, greatly improving the surface quality of aluminum profiles. With the acid-etched matt process, the aluminum melt loss is between 0.5% and 0.8%, which reduces the production cost to less than half of the traditional matt process, and the production efficiency has a substantial increase, which is of great practicality. Economic Value.
2, etching mechanism
Etching is chemical etching under certain conditions. The aluminum profile contacts the etching solution and reacts rapidly to form the complex in a very short time. The reaction equation is as follows:
3F-+A1-A1F3
6F-+A13+-A1.F63-
A1F63-+A12O3·3H2O-A13(OH)3F6+30H-
The resulting complex has a certain viscosity and easily adheres to the surface of the aluminum substrate to form a protective film. Extruded profiles generally have many slight marks. They are peaks observed under high power microscope. The protective film adhering to the aluminum matrix is ​​thicker in the recesses, thinner at the bulge, and has a greater chance of contact with the etching solution at the thin parts. , can continue to dissolve faster; thick areas are shielded by adherents to slow down the dope reaction rate, due to the difference in the rate of dissolution of the concave and convex parts, so as to achieve a smooth surface, eliminate extrusion marks (sand surface) Asia Light effect. Relieving coarse grain and weld line is directly related to the specific properties of acid etching. In the production of aluminum profiles, coarse grain and weld line are closely related to the die, extrusion process and the homogenization of cast rods. The deeper the alkali etching, the more severe the coarse crystal and the weld line. Due to the fast acid etching time and short time, the reaction has ended without severe coarse crystal and weld line, so the acid etching process can effectively relieve the coarse crystal and the weld line.
Acid etching additives in the acid etching process has the following main aspects: (1) Corrosion Inhibition: Due to the fast reaction between the F- and the natural oxide film and aluminum matrix, and the reaction is severe, coarse grains and weld lines are prone to appear. Surface quality defects such as. In order to not only maintain a certain reaction speed but also not cause quality defects, organic compounds such as sodium citrate, sodium citrate, and glycerin are added to suppress the speed of acid etching, thereby achieving the corrosion inhibition effect. (2) Leveling effect: Extrusion profiles have a lot of slight marks, which are observed at high magnification under the peaks. Adding trisodium phosphate, diatomaceous earth, polyhydric alcohols and other compounds can protect the profile bottoms of the profiles. Flatten to achieve a leveling effect. (3) Promoting effect: The addition of accelerating agent can fully spread the acid etching additive into the bath, and effectively enter the inner surface of the aluminum substrate covered by the complex, so that the reaction can be continued so as to avoid uneven corrosion of the profile. (4) The role of surfactants; The addition of surfactants such as sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate and sodium lauryl sulfate can further enhance the degreasing ability, and generate a layer of foam on the surface of the bath to suppress heat loss and troughs. Liquid volatilization, more important role is to increase the stability of the bath, because the negatively charged surfactant can be adsorbed around the particles, so that the particles produce electrostatic reaction force, so that the particles can be well suspended in the bath and not easy to precipitate . (5) Role of metal ions: Adding metal ions such as Cu2+ and Ag+ can prevent over-corrosion and make the effect of sand surface more delicate, uniform, and clear sand surface.
3, test
3.1 Test purpose
Through the acid etching and alkaline etching process test of aluminum profiles, the surface quality of the profile obtained by the two processes and the amount of aluminum dissolved in the production process are compared.
3.2 Test materials
Take the same batch of curtain wall profiles of the same model size as the test material. Curtain wall profiles, especially those with large geometric dimensions and thicker wall thicknesses, are prone to defects such as coarse grains and weld lines after the conventional alkali etching. They are representative of acid and alkali etching process tests.
3.3 Test content
3.3.1 alkaline etching process test
Two samples were taken for alkali etching in an alkaline solution, and the other processes were operated in a conventional oxidation process. Alkali corrosion process test requirements are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 alkali corrosion process test requirements
3.3.2 acid etching process test
Two specimens were etched in an etching solution. After the profile has been etched, washed, it is alkali-washed in caustic solution for 1 min, and other processes are operated by conventional oxidation processes.
3.4 Test Results and Analysis
Observe the surface conditions of the 1# and 2# samples prepared by the alkaline etching process. The surface of 1# sample is finely surfaced with slight squeezing marks. The coarse crystal and weld line are not obvious. The surface of 2# sample is clear on the surface of sand, and no extrusion marks are visible. However, there is slight coarse crystal and the weld line is exposed. . It shows that with the increase of alkali etching time, the extrusion marks of the profile surface are flattened and the sand surface is more detailed and uniform, but defects such as coarse grain and weld line are easily exposed.
Observe the surface state of the 3# and 4# samples prepared by the acid etching process. The surface quality of the two sample parts is almost the same, and all of them show that the sand surface is delicate and soft, and the existence of extrusion marks, coarse crystals, and weld lines can hardly be seen. It shows that the acid etching process can make the profile get a good quality of the sand surface in a few minutes, the extrusion marks are eliminated, the welding line can be effectively covered, the coarse grain phenomenon is relieved, and the profile surface is not easy with the increase of etching time. Has caused corrosion.
The wall thickness of the 1# and 2# specimens before oxidation was measured to be 3.0mm, that of the 1# specimen after oxidation was 2.96mm, and that of the wall thickness was 0.04mm; the wall thickness of the 2# specimen was 2.92mm, and the wall thickness was measured. Loss of 0.08mm. It shows that the time of alkali corrosion increases, the amount of corrosion of the profile increases, and the production of the matt profile of sand surface is more than 3%.
The wall thickness of the 3# and 4# specimens before oxidation was 3.0mm, that of the 3# specimens after oxidation was not less than 2.99mm, and the wall thickness loss was not more than 0.01mm; the wall thickness measured on the 4# specimen was 2.99 Mm, loss of wall thickness does not exceed 0.01mm. It shows that the time of acid etching increases, the amount of aluminum in the profile increases little, and the matt profile of sand surface is produced. The amount of acid-solubilized aluminum is above 0.5%.
3.5 Test conclusion
From the above test results and analysis, it can be concluded that the use of acid etching process for aluminum oxide surface treatment is feasible. Compared with alkaline etching, the loss of aluminum material after matt surface treatment of sandstone profiles is greatly reduced, and the surface quality of the profiles is improved, the pretreatment time is shortened, the production efficiency is improved, and the overall cost is reduced.
4, production applications
4.1 Process flow
Degreasing-washing-etching-washing-alkali washing-washing-washing-neutralization-washing-conventional anodizing
(recycle filtering when etching
After the aluminum section is degreased and rinsed, it enters the etching process. Etching and washing with water followed by caustic washing for 30 s to 1 min to remove surface-bound complexes. Anodic oxidation (coloring) and sealing treatment are performed in the normal oxidation step after washing, neutralization, and the like.
The filter device can effectively ensure the slag removal effect of the bath. Some manufacturers circulating filtration device is only a plate and frame filter press. With the increase of filter residue, the circulation flow rate of the bath liquid is insufficient, resulting in bad slag removal and affecting the use of bath liquid.
4.3 Common Faults and Countermeasures
(1) surface a little spot
Partial spot spots appear on the surface of the profile, indicating that the slag in the bath is bad, and there are aluminum slags in the etched pit. It is necessary to improve the liquid discharge method and increase the amount of aluminum slag recovered.
(2) Matte surface
The surface of the produced profile is rough and matt, indicating that the content of the accelerator in the acid etching additive is insufficient, and the content of the accelerator must be added.
(3) Mechanical pattern on the surface
The surface of the produced profile has mechanical lines, indicating that the etching time is not enough, or the content of acid etching additives in the bath is low, and the content of ammonium hydrogen fluoride or additives must be added.
(4) Surface over-corrosion
Excessive corrosion of the profile surface indicates that the etching time is too long, or the content of corrosion inhibitor and metal ions in the acid etching additive is insufficient. The etching time needs to be adjusted, and the content of the acid etching additive in the bath is supplemented.
5. Concluding remarks
The application of acid etching surface pretreatment technology has received good surface quality effects and considerable economic benefits. In order to improve the surface quality of products, reduce production costs and open up new ways for intensive and intensive production.
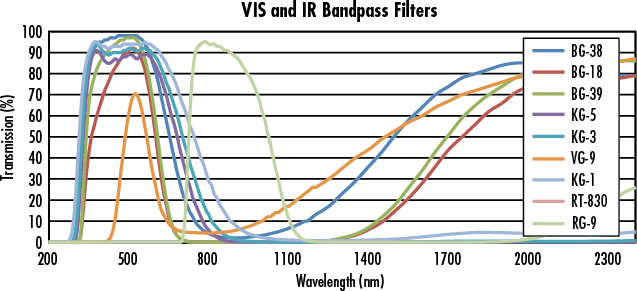
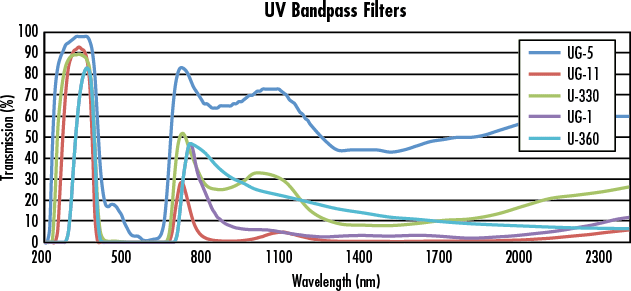
Material:Filter Glass,BK7
Dimension: 4mm-160mm - 0.20mm
Squares/Rectangles:1mm-165mm
Thickness:0.5mm-4mm
Wavelength range:190nm to 4.5um
Thickness tolerance:+/-0.01mm-0.1mm
Edges:Fine
Ground Flatness:Up to Lambda/10
Surface quantity: 80/50-20/10 Scratch/Dig
Application of Surface Pretreatment Technology for Etched Aluminum Profiles
Abstract : This paper briefly introduces the matting process of acid etching sand surface, expounds the mechanism of acid etching and the effect of acid etching additives. Through the comparison of acid etching and alkaline etching process tests, the differences between the two processes are examined and the production of acid etching technology is discussed. The application was described.